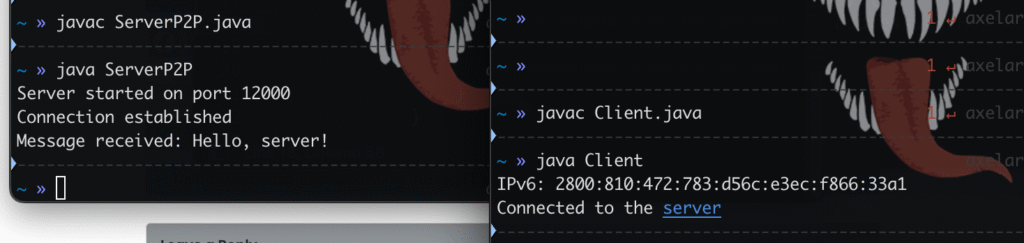
One PC is a server, the other is a client, they communicate using the public IP IPv6.
The example is implemented in Java
Attention: The Java file must have the same name as the class and respect upper and lower case.
First the server must be listening on a port:
java code ServerP2P.java:
import java.net.*;
import java.io.*;
public class ServerP2P {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
// Create a server socket on port 15000
ServerSocket serverSocket = new ServerSocket(15000);
System.out.println("Server started on port 15000");
// Accept connections
Socket socket = serverSocket.accept();
System.out.println("Connection established");
// Send and receive data
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(socket.getInputStream()));
PrintWriter writer = new PrintWriter(socket.getOutputStream(), true);
// Send message
writer.println("Hello from server");
// Receive message
String mensaje = reader.readLine();
System.out.println("Message received:" + mensaje);
// Close sockets
socket.close();
serverSocket.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("Error: " + e.getMessage());
}
}
}compile the file
javac ServerP2P.javathen run the code:
java ServerP2P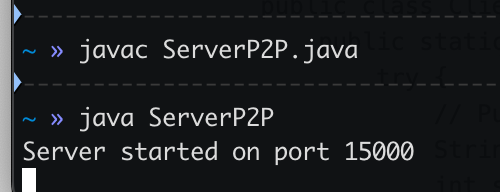
In the following example “2801:812:572:793:743f:8544:f9d4:45d” is the public IPv6 IP, replace it with the public IPv6 IP you want, you can find it on the following pages:
java code of ClientP2P.java:
import java.net.*;
import java.io.*;
public class ClientP2P {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
// Public IP address of the server
String ipServer = "2801:812:572:793:743f:8544:f9d4:45d9";
int serverPort = 15000;
// Connect to the server
Socket socket = new Socket(ipServer, serverPort);
System.out.println("Connected to the server");
// Send and receive data
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(socket.getInputStream()));
PrintWriter writer = new PrintWriter(socket.getOutputStream(), true);
// Receive message from the server
String message = reader.readLine();
System.out.println("Message received:" + message);
// Send message to the server
writer.println("Hello from client");
// Close socket
socket.close();
} catch (UnknownHostException e) {
System.out.println("Error: Server not found");
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("Error: " + e.getMessage());
}
}
}compile the code in other PC:
javac ClientP2P.javarun the compiled code:
java ClientP2P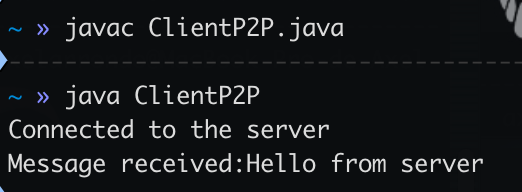
all working together:
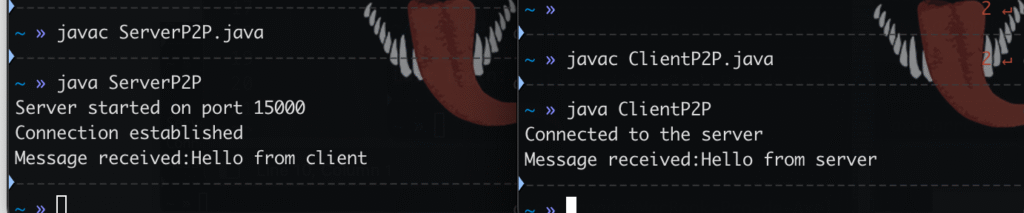
(DDNS) dynamic url mapped to public ip ipv6
tcp.from-ar.com is mapped to an IPv4 and IPv6 with dyn. (works only with IPv6)
java code:
import java.net.*;
import java.io.*;
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
String domain = "tcp.from-ar.com";
int serverPort = 12000;
//Resolve domain name to IP address
// Performs domain name resolution (DNS) to
// obtain the IP address associated with the domain name tcp.from-ar.com.
InetAddress[] addresses = InetAddress.getAllByName(domain);
InetAddress iPv6Address = null;
for (InetAddress address : addresses) {
if (address instanceof Inet6Address) {
System.out.println("IPv6: " + address.getHostAddress());
iPv6Address = address;
break;
}
}
// Create a socket that connects to the server
Socket socket = new Socket();
socket.setSoTimeout(30000); // 30 seconds
socket.connect( new InetSocketAddress(iPv6Address, serverPort) );
System.out.println("Connected to the server");
// Send data to the server
PrintWriter writer = new PrintWriter(socket.getOutputStream(), true);
writer.println("Hello, server!");
// Close the socket
socket.close();
} catch (UnknownHostException e) {
System.out.println("The server could not be found");
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("I/O Error: " + e.getMessage());
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}change tcp.from-ar.com for the real DDNS