In a nutshell, first you must copy the 3 SSL files to the PC you want to install the SSL certificate on, you need to modify the Apache configuration file so that 3 locations point to the SSL files (That’s what installation is called), then restart Apache.
For this you must modify default-ssl.conf located in /etc/apache2/sites-available
When you are given an SSL certificate, there are 3 parts you must have:
certificate (.crt), key (.key) and intermediate chain (.crt)
You should generally place it in /etc/ssl
/etc/ssl is the reference location for all certificate-based security infrastructure on your system. It’s not just about order, but about a well-thought-out security architecture that ensures your certificates and keys are managed securely and efficiently.
There are 2 directories: /certs and /private
The /etc/ssl folder is to keep the SSL files organized.
It is the standard and secure location where Linux-based operating systems store certificates, keys, and other files related to SSL/TLS cryptography.
You must modify the directories where the following lines are:
- in /certs you must place the certificate and the intermediate chain, It is a library of trusted certificates.
- in /private you must place the private key, this is the most important and sensitive place. The private keys for your own certificates are stored here. Unlike certificates, which are public, private keys must remain absolutely secret. Therefore, this directory has very restricted access permissions, often only for the root user.
SSLCertificateFileSSLCertificateKeyFileSLCertificateChainFile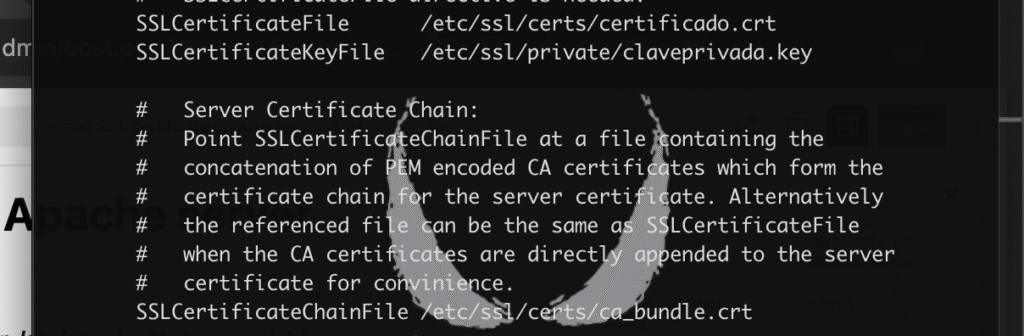
In my case, certificate.crt is my certificate
private key.key is the. key
ca_bundle.crt is the intermediate chain
Wherever you got the SSL certificate from, you should get the 3 files (the certificate, the key and the intermediate chain) or a .pfx (which combines the certificate and the key) and the intermediate chain separately.
Generally the .pfx has a password
After modifying the configuration file you must restart the Apache service.
sudo systemctl restart apache2The command to check that the syntax of Apache configuration files is free of errors on Ubuntu Server is:
sudo apache2ctl configtestIf everything is correct, the output will simply be:
Syntax OK
If there is an error, the command will tell you exactly where the problem is, displaying a detailed error message, for example:
Syntax error on line 25 of /etc/apache2/sites-enabled/000-default.conf: Invalid command ‘Docume’, perhaps misspelled or defined by a module not included in the server configuration