When we consult a domain we have to specify the port
in the web browser too
The web browser with ports 80 and 443 does not need to be written, the web browser does not display them
When we query port 80, the web browser ignores it and shows that you are querying with the HTTP protocol.
When we query port 443, the web browser ignores it and shows that you are querying with the HTTPS protocol.
If you enter a port (other than 80 and 443) that has an SSL certificate installed, it will say “https” and the entered port will be displayed.
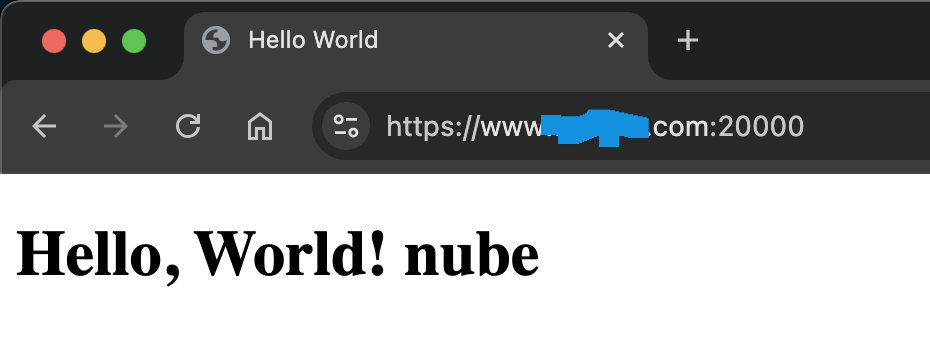
I don’t enter https://, it just says that, I start with www
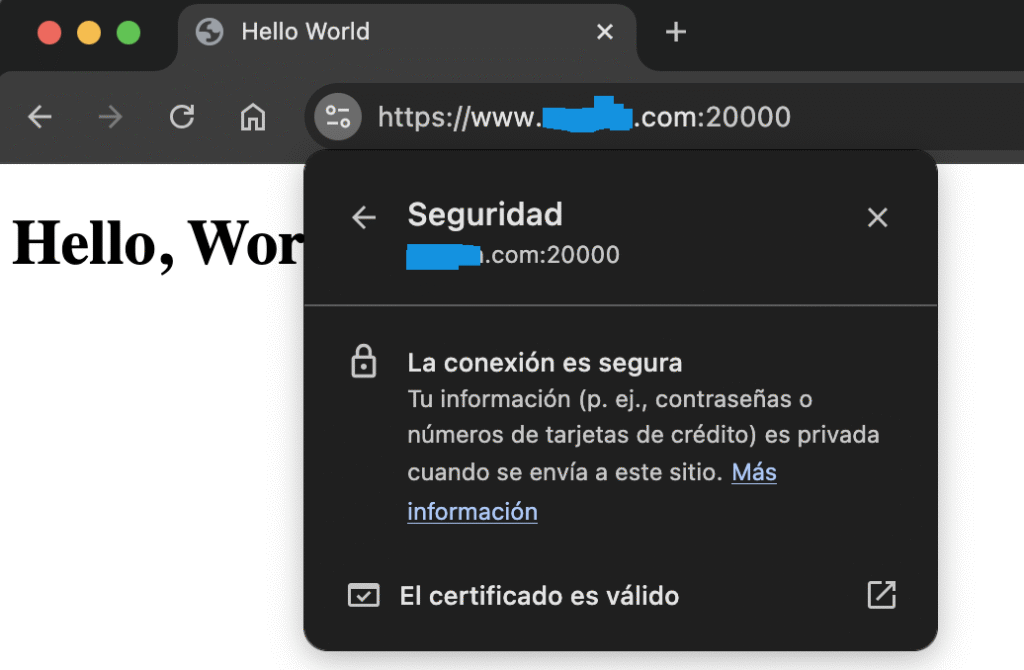
An SSL certificate makes the HTTP protocol become HTTPS
Both HTTP and HTTPS are fundamental communication protocols for the web.
The main and most important difference between the two is security.
HTTP: It’s the Hypertext Transfer Protocol. It’s the original and standard method for sending and receiving data over the web.
Sends and receives information in plain text. This means that data, such as passwords, usernames, or any other information, is not encrypted.
It’s an insecure protocol. If a third party intercepts the communication between your browser and an HTTP server, they can easily view and read all the information. This makes it vulnerable to man-in-the-middle attacks.
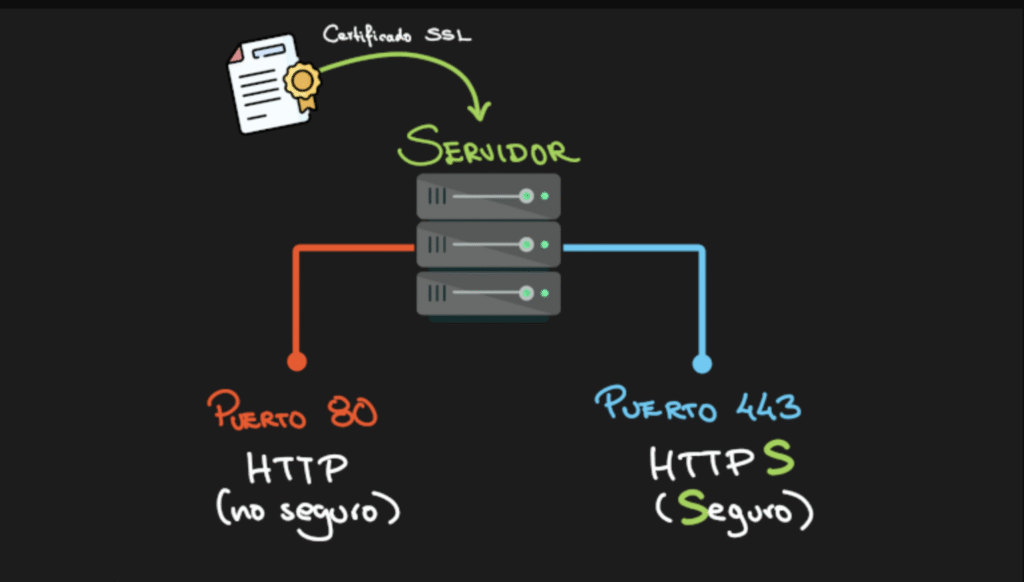
Web addresses using HTTP begin with http://
Use port 80.
HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure)
It’s the secure version of the HTTP protocol. The “S” at the end stands for “Secure.”
It adds a layer of security through SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) or, more commonly today, TLS (Transport Layer Security) protocols. These protocols encrypt communication, making data unreadable to anyone who intercepts it.
It’s a secure protocol. By encrypting information, it protects the privacy and integrity of the transmitted data. It’s essential for any website that handles sensitive information, such as online stores, banks, social networks, etc.
In addition to encryption, HTTPS also authenticates the identity of the web server. This is done through a digital certificate issued by a Certificate Authority (CA). The certificate verifies that the website is who it claims to be, which helps prevent phishing attacks.
Web addresses using HTTPS begin with https://. Modern browsers display a lock icon in the address bar to indicate a secure connection.
Use port 443.
Today, the use of HTTPS has become a de facto standard. Search engines like Google prioritize websites that use HTTPS, and many browsers display security warnings for sites that still use HTTP.